Many people don’t always understand what value is placed on the knowledge of corrosive incidents. They hear the term corrosive and some people immediately think of acids. In reality, acids are only one end of the scale.
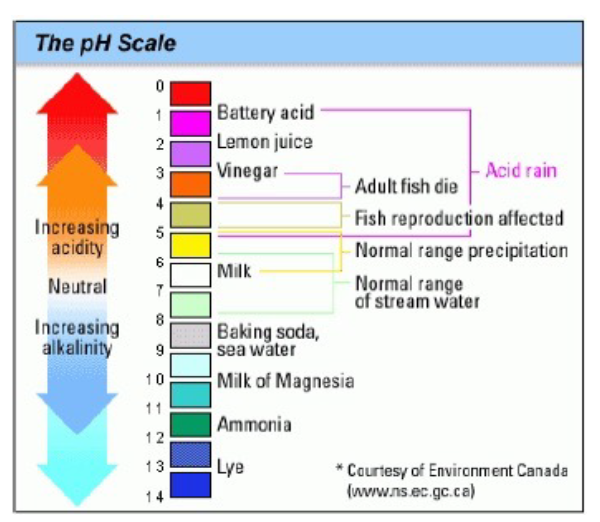
The PH scale runs from 0-14 with 7 being neutral. Acids are on the lower end of the scale with the acidic materials having a PH of 0-6.9. Caustics or bases as sometimes called are on the higher in the scale with caustic materials having a PH of 8-14. DOT considers any material with a PH of 5-9 to be non-hazardous.
All crew must get an SDS any time a product is labeled as a class 8 corrosive material. Crew must also have pH paper, Acid / water solution, or Base / neutralizer agent, poly sheeting, poly drums, poly scoops, shovels, and a 5-gas monitor.
PPE should be Level B or C (combination vapor APR cartridges, See SDS) PPE and respiratory recommendation should be selected by reviewing the suit compatibility charts as well as the SDS. Any deviation from recommended PPE must be justified through testing, monitoring and documenting of actual hazards or lack of hazards found.
To mitigate the hazard, crews will need to neutralize the product so that it is no longer a hazard.
If the PH of a product is below a 5 and you need to neutralize the product, you would then need to neutralize the acid to raise the PH scale. Generally, the stronger the acid, the stronger the base will need to be to neutralize it. If using a weaker base, more products will be needed. Neutralization can only occur with water present to transfer Hydrogen ions, so water will be needed to add to solid base neutralizers. Planning is important when neutralizing; the acid will undergo a chemical reaction with the neutralizer forming a completely new chemical. Though the original acid may be neutralized, the end product may also be hazardous.
If the PH of a product is above a 9 and you need to naturalize the product. You will need to neutralize the base to lower the PH scale. If using a weaker acid as a neutralizer, more products will be needed. Neutralization can only occur with water present to transfer Hydrogen ions, so water will be needed to add to solid-base neutralizers. Planning is important when neutralizing; the base will undergo a chemical reaction with the neutralizer forming a completely new chemical. Though the original base may be neutralized, the end product may also be hazardous. FCE!